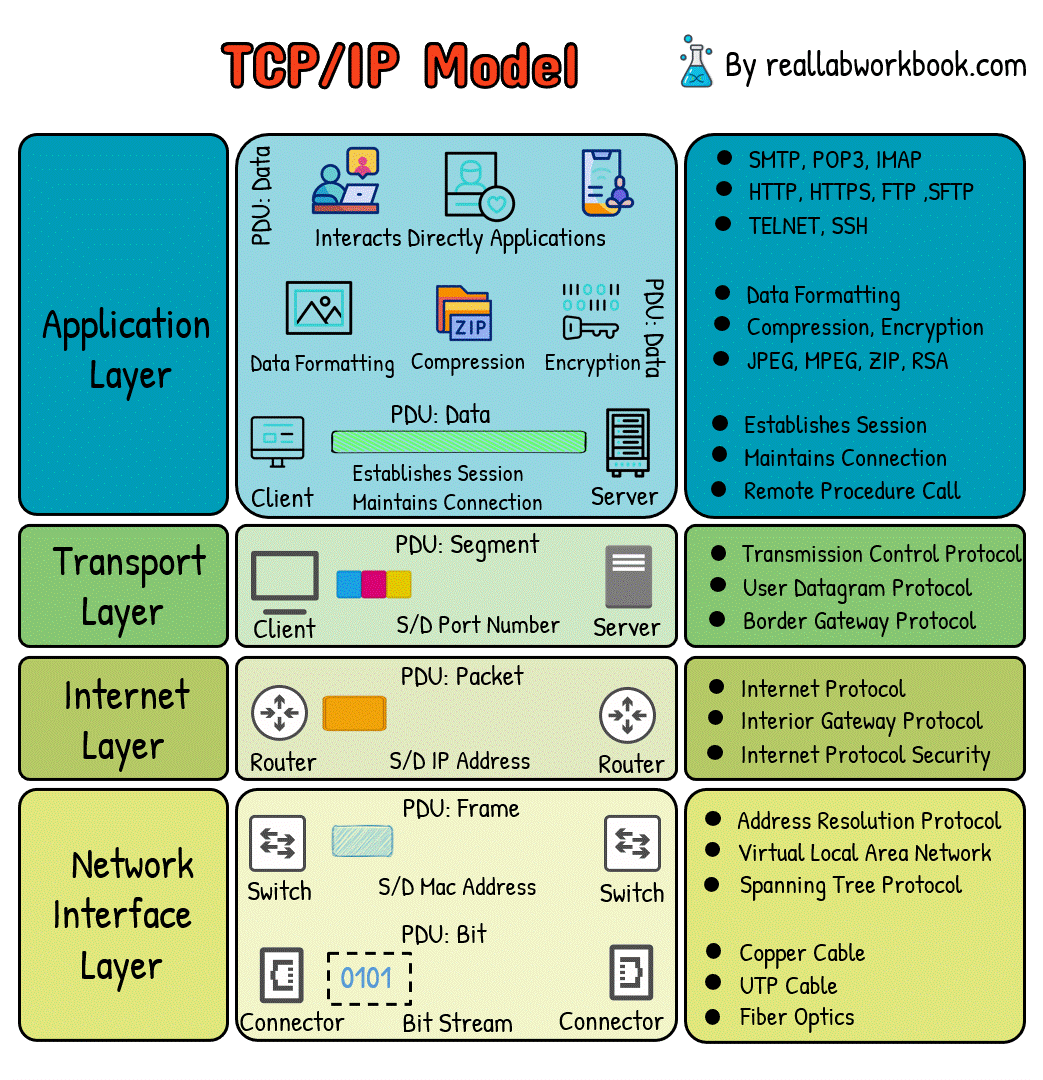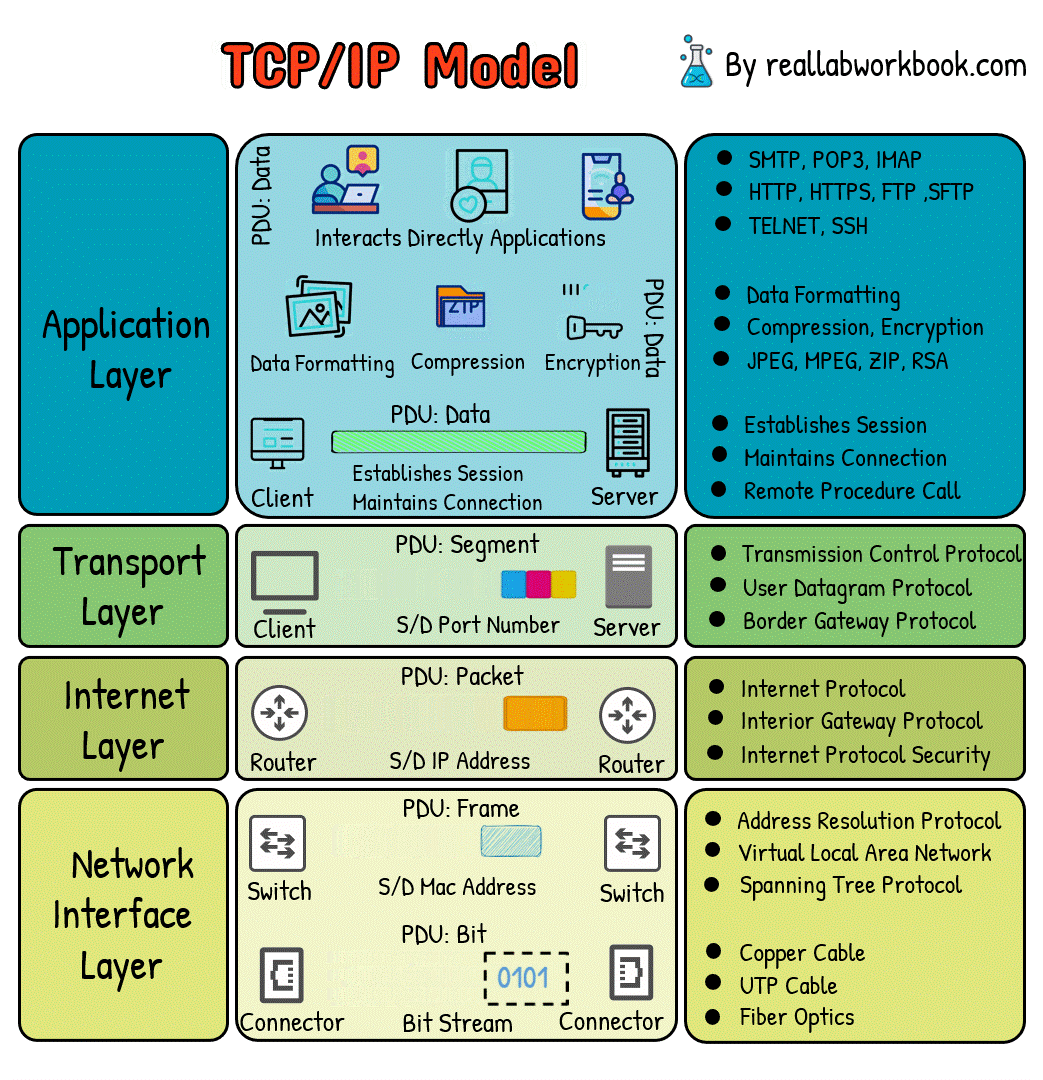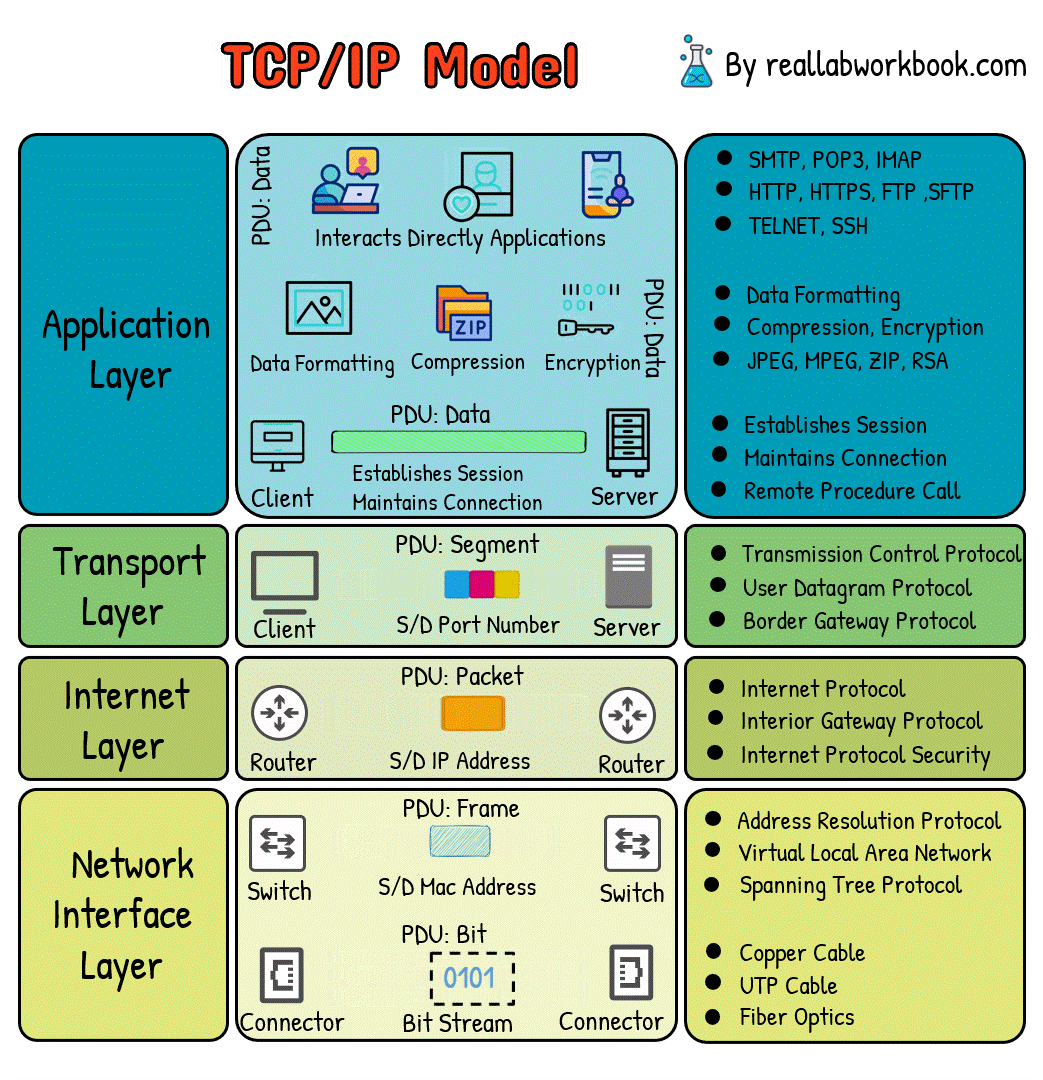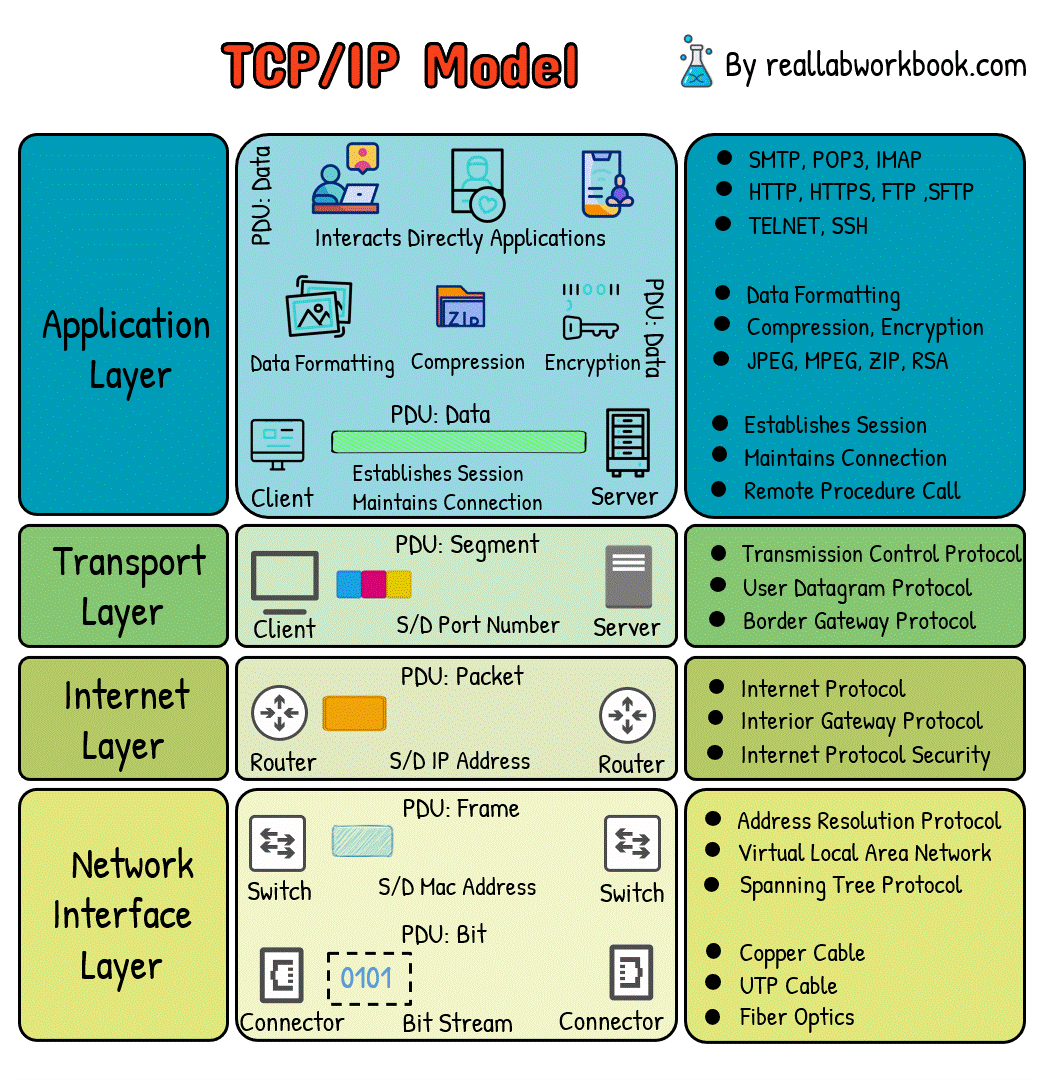
What is TCP/IP Model
Pass Any Cisco Exam On Your First Try.
Want to boot your networking career ? This is the chance for you.
The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) model is a concise and practical networking model used for the implementation of internet protocols and is the foundation of the modern internet. It consists of four layers:
To receive all the full articles and support Real Lab Workbook, consider subscribing:
1. Link Layer (Network Interface Layer):
The link layer deals with the physical connection between devices on the same network. It includes protocols and technologies specific to the physical medium, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol). This layer ensures that data packets are transmitted reliably across the local network.
2. Internet Layer:
The internet layer handles addressing, routing, and packet forwarding. Its primary protocol is the Internet Protocol (IP), which is responsible for addressing packets and routing them across interconnected networks. IPv4 and IPv6 are the two versions of IP in use today.
3. Transport Layer:
The transport layer is responsible for end-to-end communication between devices. It ensures that data packets are delivered reliably and in the correct order. The two main protocols in this layer are:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): Provides reliable, connection-oriented communication with features like error detection, flow control, and congestion control.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP): Offers unreliable, connectionless communication, suitable for applications where speed is prioritized over reliability.
4. Application Layer:
This layer interacts directly with applications and end-users. It includes protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS. Application layer protocols define the format and meaning of data exchanged between applications running on different devices.
The TCP/IP model is more straightforward and practical compared to the OSI model. It doesn't strictly adhere to the concept of seven layers but instead focuses on key functionalities necessary for internet communication. TCP/IP is widely used in networking, serving as the basis for communication protocols across the internet and many other networks.
One notable aspect of the TCP/IP model is its flexibility, which allows it to adapt to various networking technologies and environments. Additionally, TCP/IP's modular design enables the addition of new protocols and technologies without requiring a complete overhaul of the existing infrastructure, contributing to its longevity and widespread adoption.