What is Network ?
Pass Any Cisco Exam On Your First Try.
Want to boot your networking career ? This is the chance for you.
A network is a collection of interconnected devices or nodes that communicate and share resources with each other. These devices can include computers, servers, routers, switches, printers, and other hardware components. Networks facilitate the exchange of data, information, and resources among connected devices, enabling communication and collaboration.
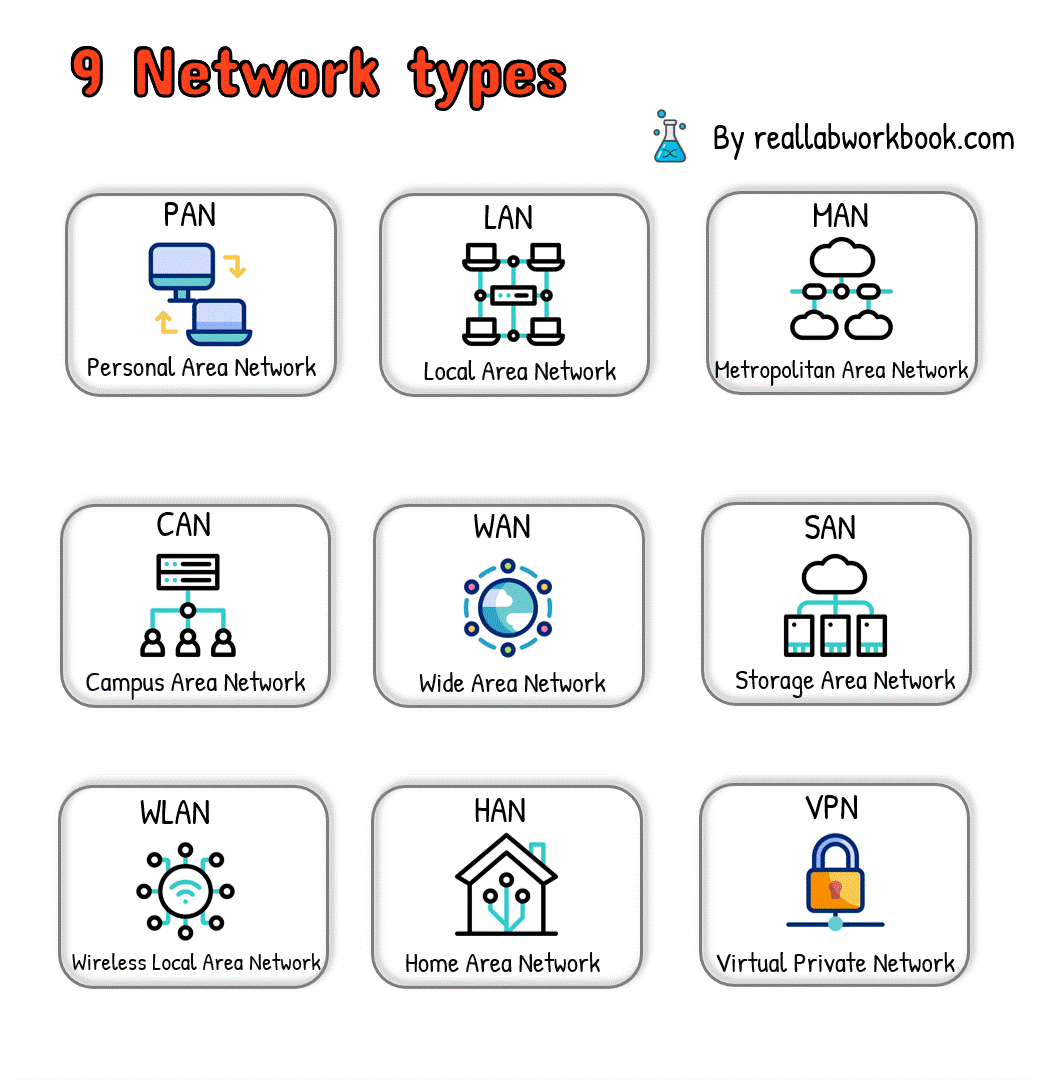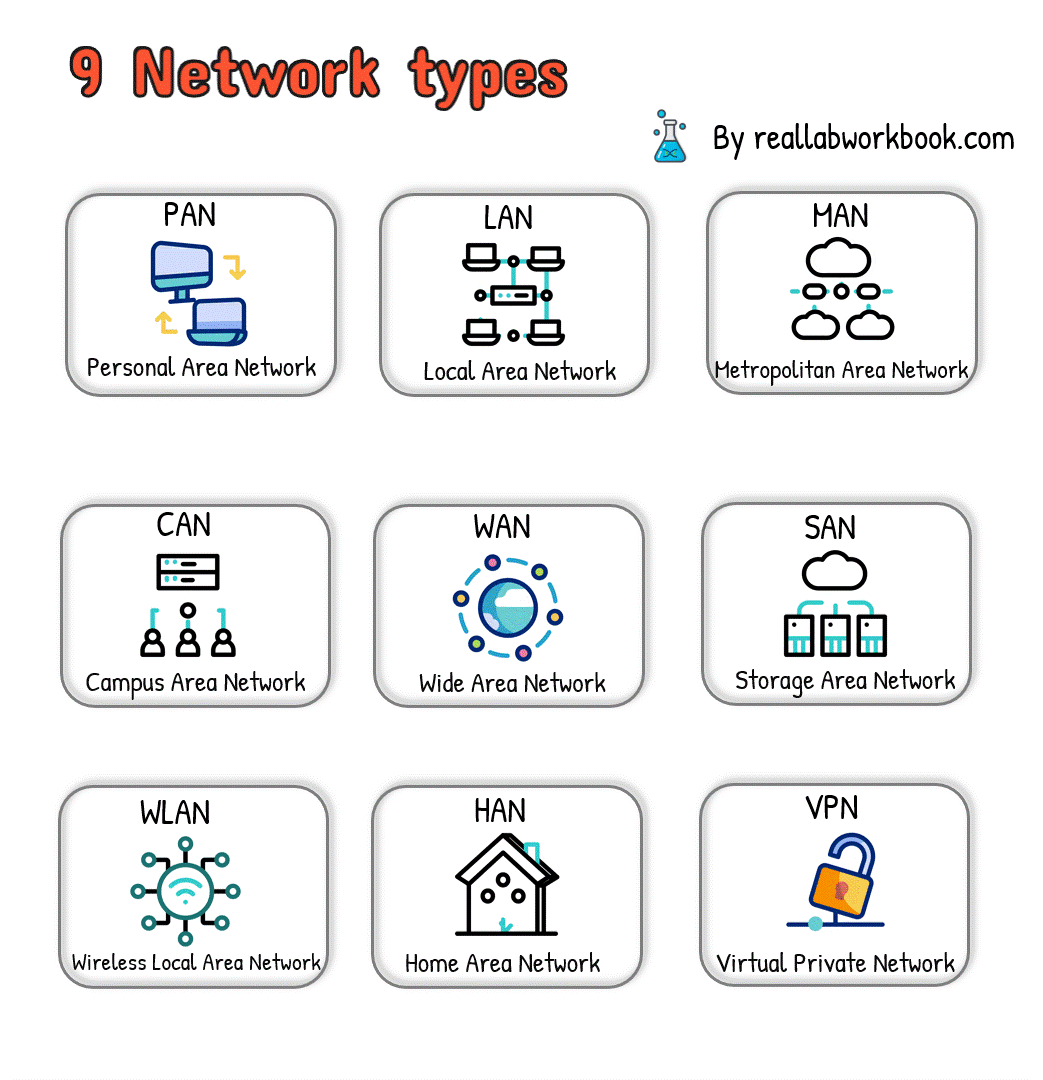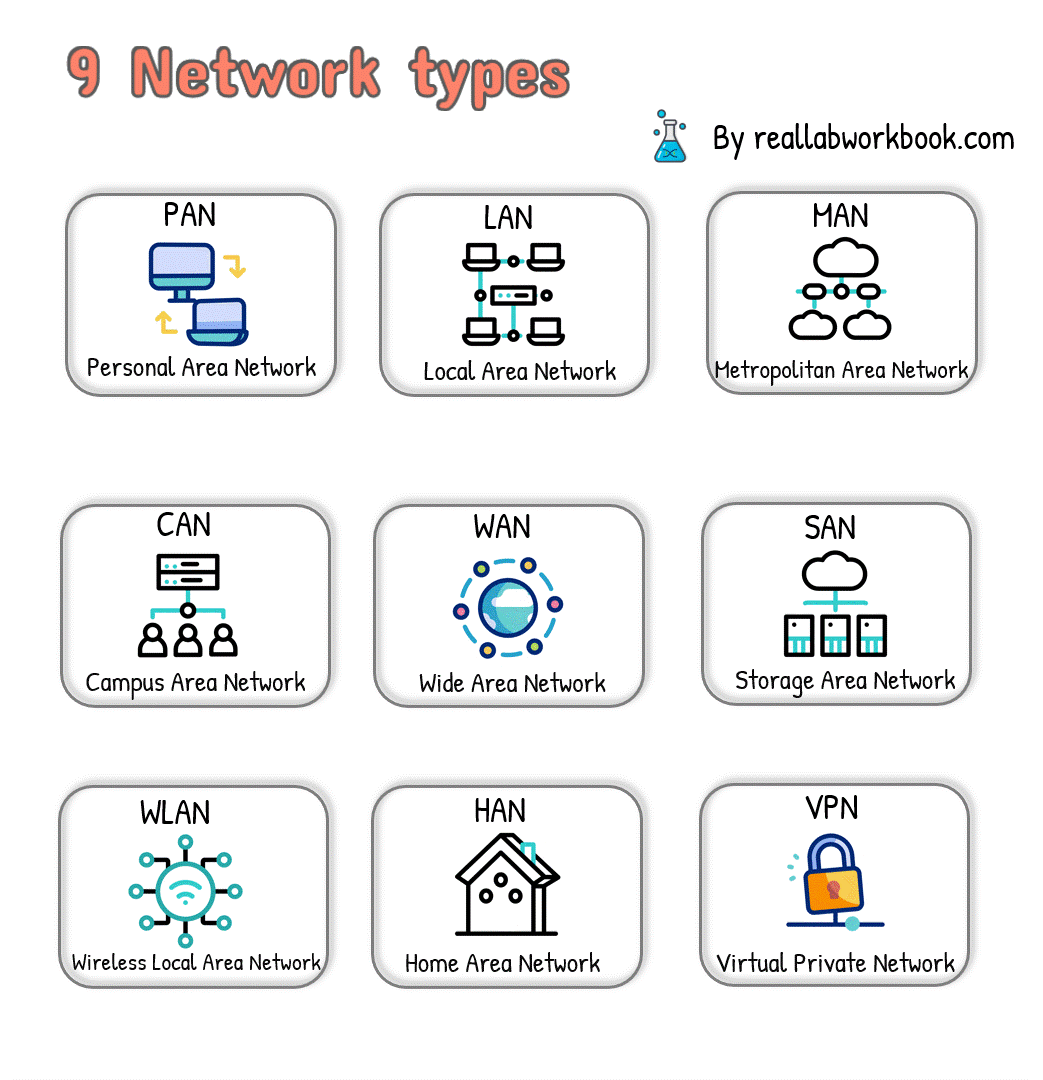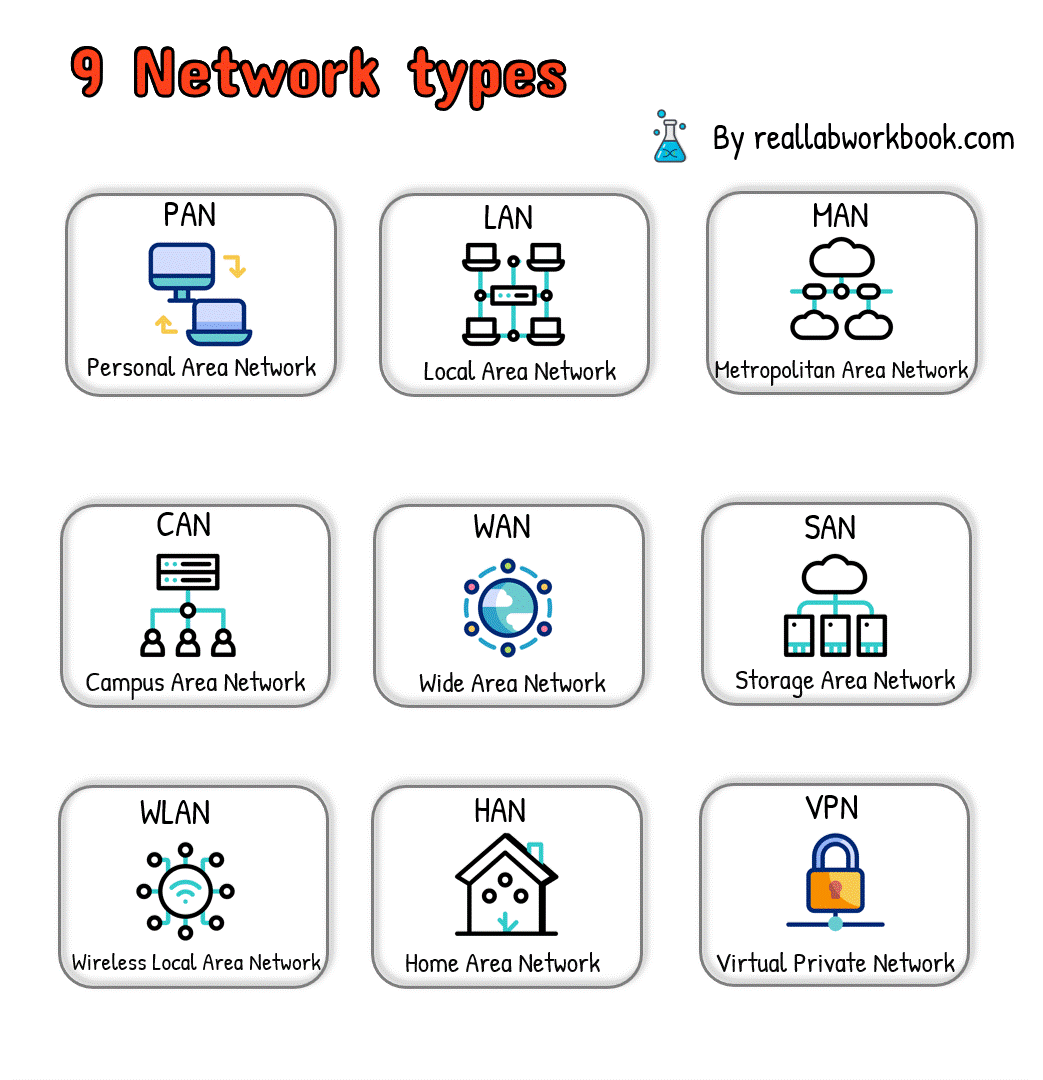
Here are nine types of networks:
To receive all the full articles and support Real Lab Workbook, consider subscribing:
1.Local Area Network (LAN):
A LAN connects devices within a small geographic area, such as a single building, office, or home.
LANs typically use Ethernet cables or wireless connections for communication.
Examples include office networks, home networks, and school networks.
2.Wide Area Network (WAN):
A WAN spans a large geographic area, connecting multiple LANs or other networks over long distances.
WANs use various technologies, including leased lines, fiber-optic cables, and satellite links.
The internet is the most prominent example of a WAN.
3.Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
A MAN covers a larger geographical area than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, such as a city or metropolitan area.
MANs connect multiple LANs and facilitate high-speed data exchange within the region.
MANs are commonly used in urban areas for interconnecting local networks.
4.Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN):
A WLAN uses wireless communication technology, such as Wi-Fi, to connect devices within a limited area without the need for physical cables.
WLANs provide mobility and flexibility for connected devices and are commonly used in homes, offices, and public spaces.
5.Personal Area Network (PAN):
A PAN connects devices within the immediate vicinity of an individual, typically within a range of a few meters.
Examples include Bluetooth connections between smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
PANs facilitate data exchange and synchronization between personal devices.
6.Campus Area Network (CAN):
A CAN interconnects multiple LANs within a university campus, corporate campus, or large educational institution.
CANs facilitate communication and resource sharing among departments or buildings within the campus.
7.Storage Area Network (SAN):
A SAN is a specialized network that provides access to storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries, over high-speed connections.
SANs are used to centralize storage resources and provide scalable and reliable storage solutions for businesses and organizations.
8.Virtual Private Network (VPN):
A VPN extends a private network across a public network, such as the internet, allowing users to securely access resources remotely.
VPNs use encryption and tunneling protocols to ensure data privacy and security.
9.Home Area Network (HAN):
A HAN connects devices within a household, enabling communication and resource sharing among family members.
HANs typically include devices such as computers, smartphones, smart TVs, and home automation systems.
These are some of the various types of networks that serve different purposes and cater to different communication and connectivity needs.