Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN): Revolutionizing Modern Networking
Pass Any Cisco Exam On Your First Try.
Want to boot your networking career ? This is the chance for you.
Introduction to SD-WAN
Core Components of SD-WAN
Virtualization and Overlay Networking:
SD-WAN abstracts the underlying hardware, creating virtual networks on top of physical infrastructure. This overlay approach enables flexibility in routing traffic across various connection types, including MPLS, broadband, and LTE.Centralized Control and Management:
A hallmark of SD-WAN is its centralized orchestration, providing administrators with a single dashboard to monitor, configure, and manage the network. Policies can be defined at the central controller and pushed to all network nodes, reducing the complexity of manual configurations.Application-Aware Traffic Steering:
SD-WAN intelligently identifies and prioritizes traffic based on application requirements. Critical applications like video conferencing or VoIP can be routed through low-latency links, while less sensitive traffic utilizes cost-effective broadband.Dynamic Path Selection:
Traditional WANs often rely on static routing protocols, leading to inefficiencies during link degradation. SD-WAN continuously monitors link performance, dynamically rerouting traffic to maintain optimal performance and reliability.Enhanced Security Features:
SD-WAN integrates robust security measures such as encryption, next-generation firewalls, and micro-segmentation. These features protect data across multiple endpoints and ensure compliance with stringent regulations.
Key Benefits of SD-WAN
Cost Efficiency:
By leveraging broadband connections like DSL or LTE alongside MPLS, SD-WAN significantly reduces operational costs. Organizations can optimize bandwidth without solely relying on expensive private circuits.Improved Performance:
SD-WAN’s ability to prioritize and route traffic based on application needs enhances overall performance. This is particularly valuable for latency-sensitive applications like real-time collaboration tools and video streaming.Simplified Management:
Centralized orchestration reduces administrative overhead. Network administrators can deploy, monitor, and update policies across a distributed network from a single interface.Scalability:
SD-WAN facilitates easy scaling of networks, making it ideal for organizations with geographically dispersed branches. Adding new sites involves minimal configuration compared to traditional WAN setups.Cloud Optimization:
With direct access to cloud services and data centers, SD-WAN eliminates the need to backhaul traffic through a central hub. This reduces latency and improves the user experience for cloud-based applications.Resilience and Reliability:
Features like dynamic failover ensure uninterrupted connectivity, even during link failures. SD-WAN continuously evaluates the health of connections and reroutes traffic as needed.
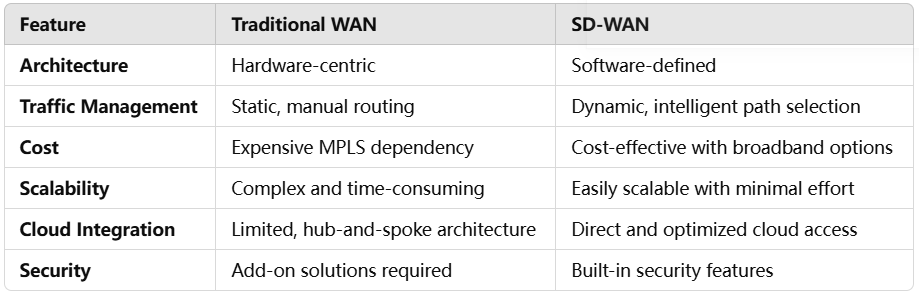
SD-WAN vs. Traditional WAN
Challenges in SD-WAN Adoption
While SD-WAN offers numerous benefits, organizations may encounter challenges during its adoption:
Initial Implementation Complexity:
Transitioning from a traditional WAN to SD-WAN requires meticulous planning and integration with existing infrastructure.Skill Gap:
IT teams may require training to manage and optimize SD-WAN solutions effectively.Interoperability Issues:
Integrating SD-WAN with legacy systems or other network components can pose challenges.Security Considerations:
Despite its robust features, SD-WAN relies heavily on internet-based connections, necessitating vigilant security measures to prevent vulnerabilities.
Use Cases of SD-WAN
Multi-Branch Enterprises:
Retail chains, banks, and healthcare organizations benefit from SD-WAN’s ability to connect multiple locations seamlessly and securely.Cloud-First Strategies:
Organizations leveraging SaaS platforms like Microsoft 365 or AWS can use SD-WAN to optimize connectivity, ensuring high performance for cloud applications.Remote Work Enablement:
SD-WAN provides secure and efficient access for remote employees, a critical requirement in the post-pandemic era.IoT Deployments:
SD-WAN enhances the connectivity and management of IoT devices by providing secure, reliable network paths.
The Future of SD-WAN
Integration with 5G:
The advent of 5G networks will amplify SD-WAN capabilities, offering ultra-low latency and high-speed connectivity.AI-Driven Insights:
AI and machine learning will enhance SD-WAN by providing predictive analytics, automated troubleshooting, and intelligent traffic management.Edge Computing:
As edge computing gains traction, SD-WAN will play a pivotal role in connecting edge devices to cloud services efficiently.Security Enhancements:
SD-WAN will integrate with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) frameworks, combining networking and security in a unified platform.