OSPF Packet Header Format Details
Pass Any Cisco Exam On Your First Try.
Want to boot your networking career ? This is the chance for you.
There are five types of OSPF packets:
Hello Packet
Database Description Packet (DD)
Link State Request Packet (LSR)
Link State Update Packet (LSU)
Link State Acknowledgment Packet (LSA)
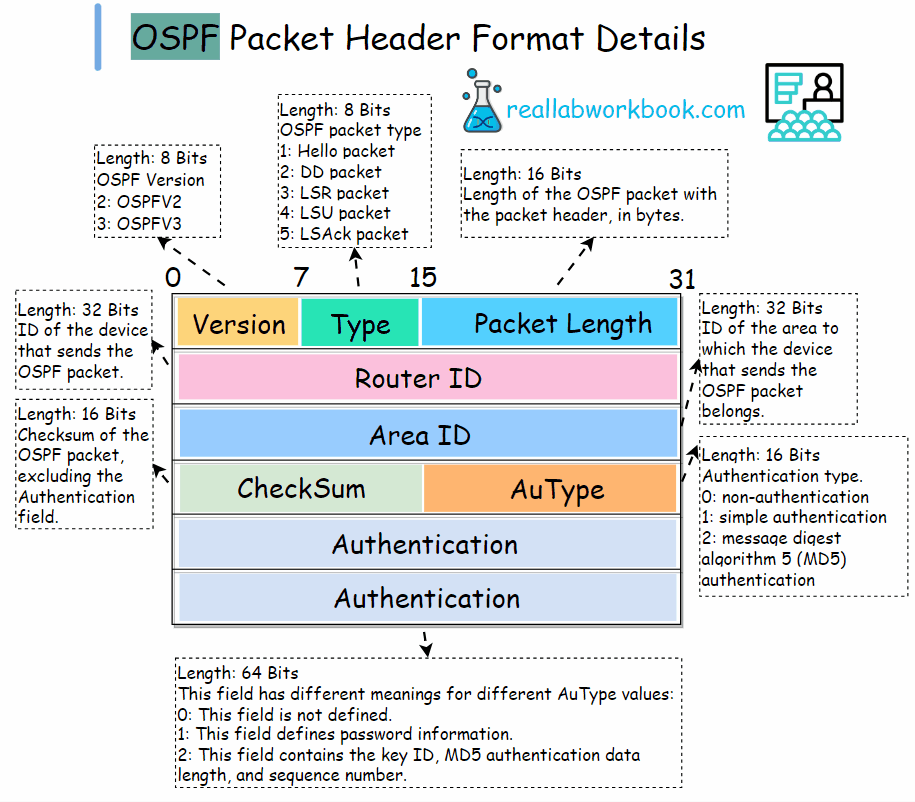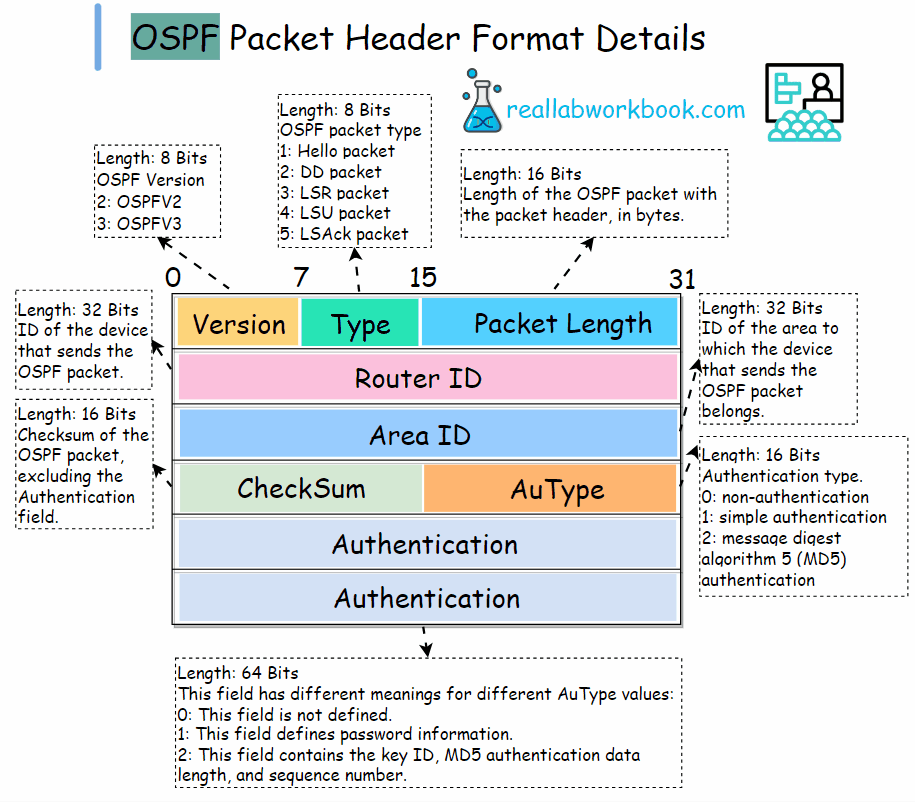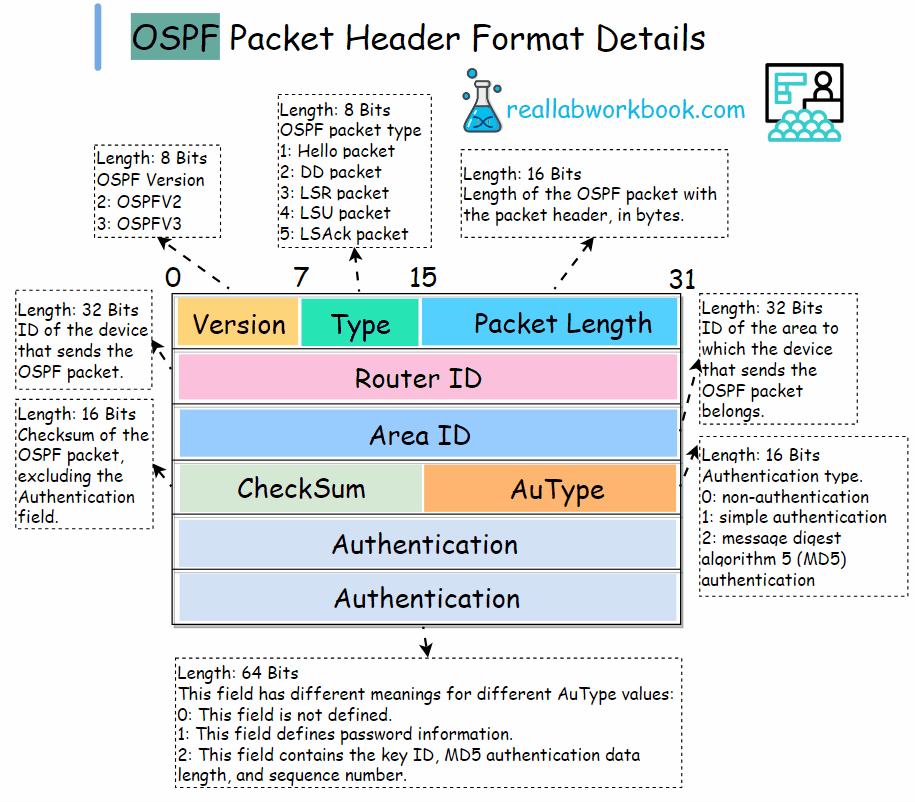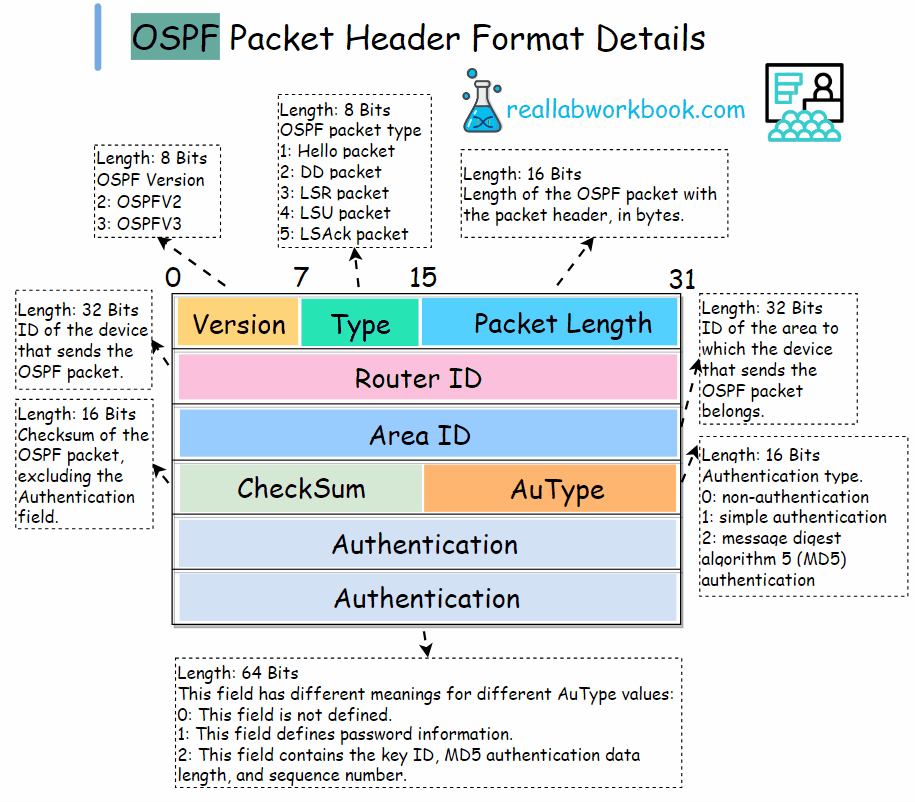
All five types of OSPF packets have the same packet header format, and the header of each type of packet is 24 bytes long.
To receive all the full articles and support Real Lab Workbook, consider subscribing:
Version: 8 bits, OSPF version number, 2 for OSPFv2, 3 for OSPFV3.
The version number field indicates the OSPF protocol version being used. It allows routers to ensure compatibility and interpret the packet correctly.
Type: 8 bits, OSPF packet type. The values are : 1.Hello packet. 2. DD packet. 3. LSR packet. 4. LSU packet. 5. LSAck packet.
The packet type field specifies the type of OSPF packet, such as hello, database description, link-state request, link-state update, link-state acknowledgment.
Packet length: 16 bits, Length of the OSPF packet with the packet header, in bytes.
The packet length field indicates the total length of the OSPF packet, including the header and the data portion. It helps routers accurately parse the packet and extract the necessary information.
Router ID: 32 bits, ID of the device that sends the OSPF packet.
The router ID field contains the OSPF router ID of the sender, which uniquely identifies the router within the OSPF domain.
Area ID: 32 bits, ID of the area to which the device that sends the OSPF packet belongs.
The area ID field specifies the OSPF area to which the packet belongs. OSPF networks are divided into areas to facilitate scalability and efficient routing. The area ID allows routers to determine the appropriate area for processing the packet.
Checksum: 16 bits, Checksum of the OSPF packet, excluding the Authentication field.
The checksum field is used to verify the integrity of the OSPF packet. It ensures that the packet has not been corrupted during transmission. Routers calculate the checksum based on the contents of the packet and compare it with the received checksum to detect any errors.
AuType: 16 bits, Authentication type. The values are: 0: non-authentication, 1: simple authentication, 2: message digest algorithm 5 (MD5) authentication
The AuType field is used to define authentication type, authentication data is not included in this field.
Authentication: 64 bits, This field has different meanings for different AuType values:
0: This field is not defined, 1: This field defines password information, 2: This field contains the key ID, MD5 authentication data length, and sequence number.
The authentication field is used to define authentication data according to each authentication type.