OSPF Builds Routing Table Process
Pass Any Cisco Exam On Your First Try.
Want to boot your networking career ? This is the chance for you.
📣 OSPF Builds Routing Table Process
To receive all the full articles and support Real Lab Workbook, consider subscribing:
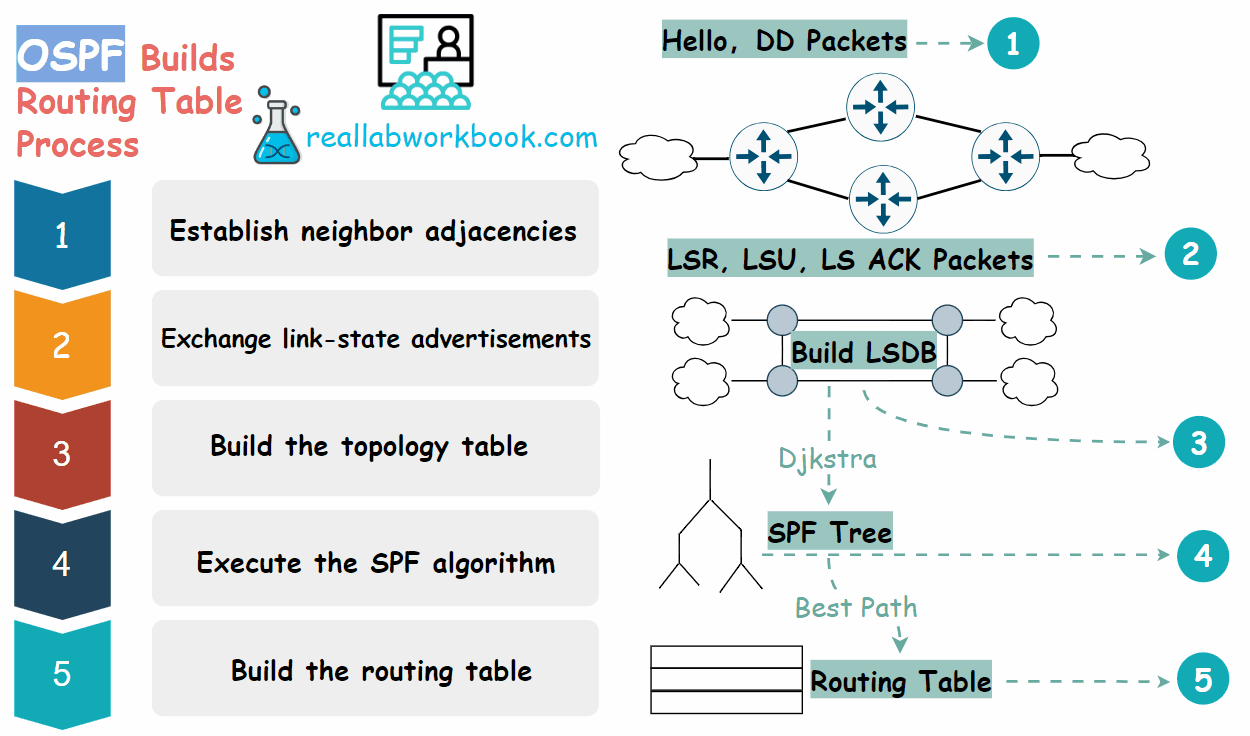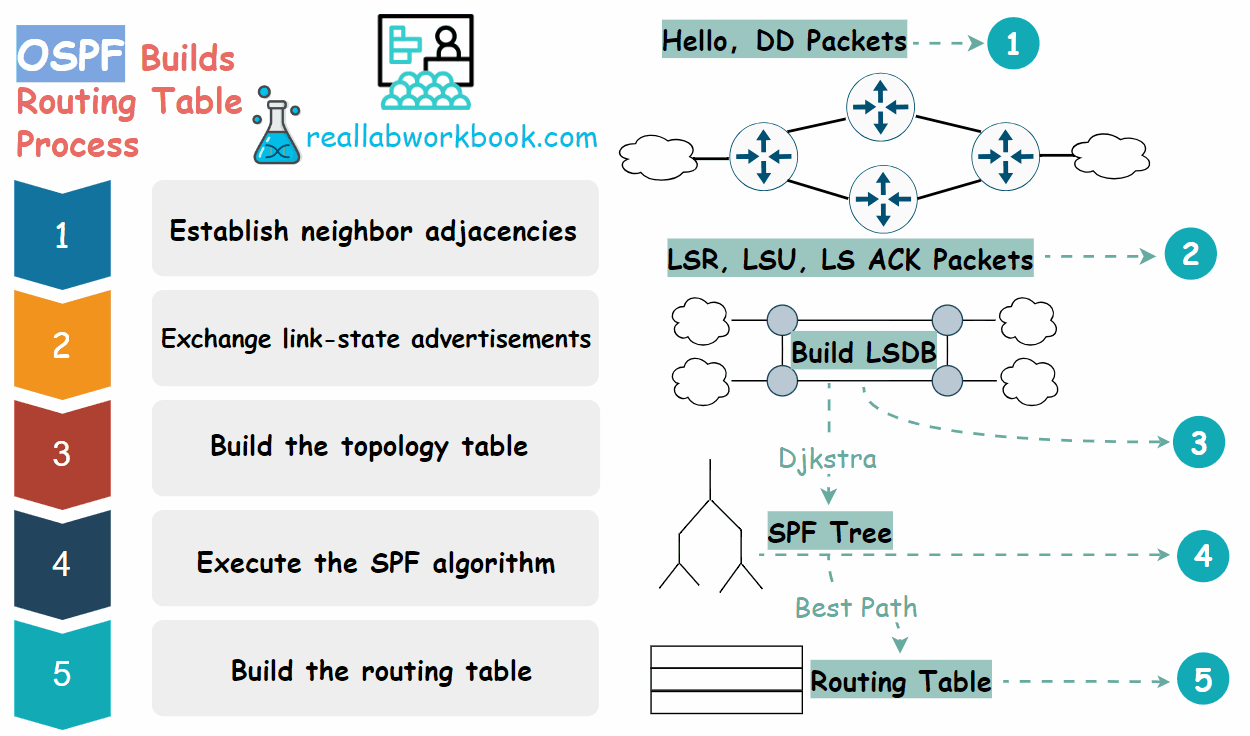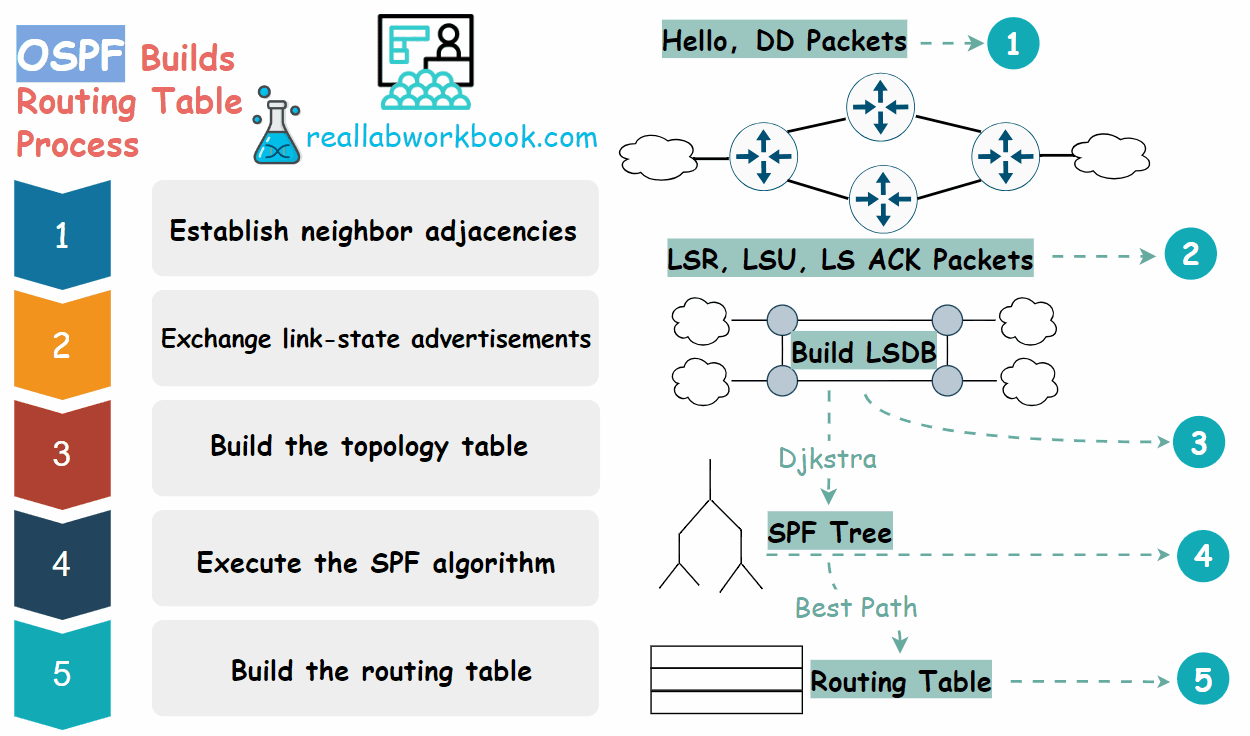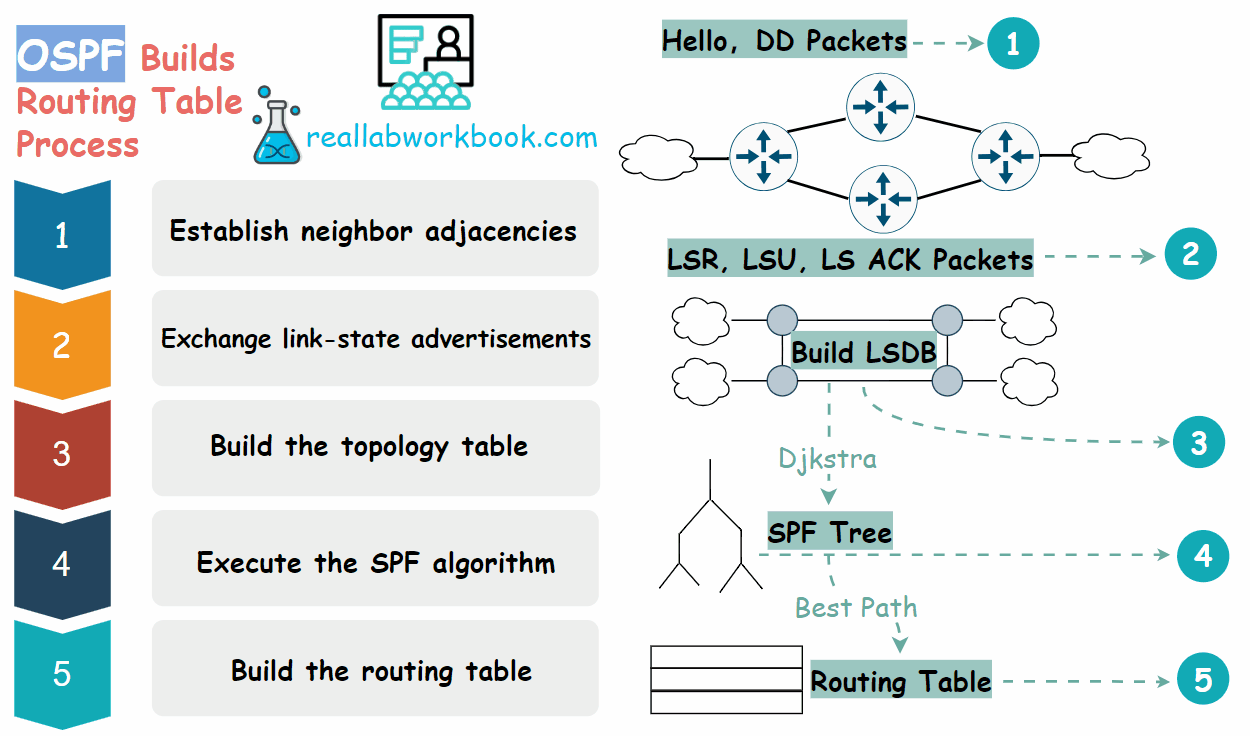
To create and maintain routing information, OSPF routers complete the following link-state routing process to reach a state of convergence.
Establish neighbor adjacencies: OSPF routers must form adjacencies with their neighbor before they can share information with that neighbor. An OSPF router sends Hello packets out all OSPF enabled interfaces to determine whether neighbors are present on those links. If a neighbor is present, the OSPF router attempts to establish a neighbor adjacency with that neighbor.
Exchange link-state advertisements: After adjacencies are established, routers then exchange link-state advertisements (LSAs). LSAs contain the state and cost of each directly connected link. Routers flood their LSAs to adjacent neighbors. Adjacent neighbors receiving the LSA immediately flood the LSA to other directly connected neighbors, until all routers in the area have all LSAs.
Build the topology table: After the LSAs are received, OSPF routers build the topology table which is called link state database (LSDB) based on the received LSAs. This database eventually holds all the information about the topology of the network. It is important that all routers in the area have the same information in their LSDBs.
Execute the Dijkstra's SPF algorithm: Routers then execute the Dijkstra's SPF algorithm. The SPF algorithm creates the SPF tree.
Build the routing table: From the SPF tree, the best paths are inserted into the routing table. Routing decisions are made based on the entries in the routing table.