DNS Attack Type
Pass Any Cisco Exam On Your First Try.
Want to boot your networking career ? This is the chance for you.
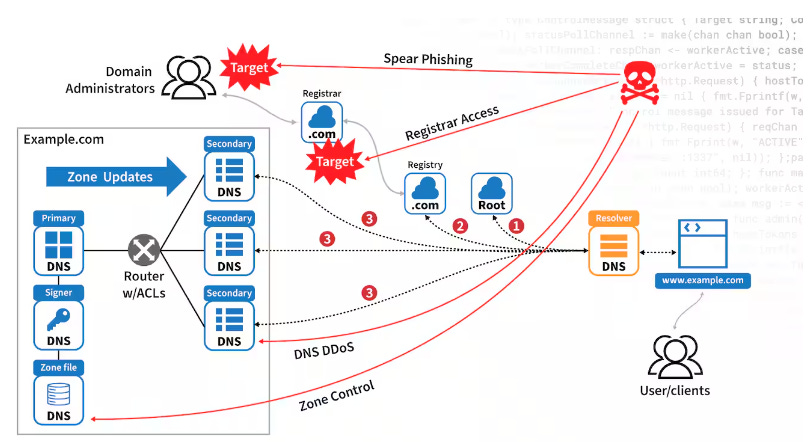
DNS (Domain Name System) attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the DNS infrastructure, which translates domain names (like example.com) into IP addresses. These attacks aim to disrupt, intercept, or redirect user traffic. Here are the main types of DNS attacks:
1. DNS Spoofing (Cache Poisoning)
Description: Attacker injects false DNS records into a resolver's cache, redirecting users to malicious sites.
Impact: Users are tricked into visiting fraudulent websites, often leading to phishing or malware distribution.
2. DNS Amplification Attack
Description: A type of DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack that leverages open DNS resolvers to overwhelm a target with large amounts of traffic.
Impact: The target's servers are rendered unavailable due to excessive traffic.
3. DNS Tunneling
Description: Encodes non-DNS traffic (e.g., HTTP) into DNS queries, often used for data exfiltration or command-and-control (C2) communication.
Impact: Sensitive data can be stolen or malicious actions executed covertly.
4. Domain Hijacking
Description: An attacker gains unauthorized control over a domain by compromising its registrar account or exploiting vulnerabilities.
Impact: The domain can be redirected, defaced, or taken offline.
5. DNS Reflection Attack
Description: Similar to amplification attacks, but it uses spoofed requests to make the DNS server send responses to the victim's IP address.
Impact: Overwhelms the victim's server, causing service disruptions.
6. NXDOMAIN Attack
Description: Overwhelms DNS resolvers by sending a high volume of queries for non-existent domains.
Impact: Depletes server resources, causing legitimate requests to fail.
7. DNS Flood Attack
Description: Inundates a DNS server with a high volume of queries to exhaust its resources.
Impact: Causes the DNS server to crash or become unresponsive.
8. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack
Description: An attacker intercepts and manipulates DNS traffic between the user and the resolver.
Impact: Users are redirected to malicious sites, potentially leading to credential theft or malware infections.
9. Registrar Hijacking
Description: Attackers compromise a domain registrar's system to alter DNS records or transfer domain ownership.
Impact: Entire domains can be taken over or redirected.
10. DNS Typosquatting
Description: Registering domains that resemble legitimate ones (e.g.,
googgle.cominstead ofgoogle.com) to exploit user typos.Impact: Users can be redirected to phishing sites or exposed to ads/malware.
11. Fast Flux DNS
Description: Frequently changing IP addresses in DNS records to avoid detection and takedown.
Impact: Used for botnets, phishing, and other malicious activities.
Mitigation Strategies:
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions): Adds cryptographic signatures to DNS records.
Rate Limiting: Limits the number of queries a DNS server can process per client.
Monitoring and Logging: Tracks DNS activity for anomalies.
Firewalls and Access Control: Blocks malicious traffic and restricts open resolvers.
Patch Management: Keeps DNS server software up-to-date.